Search Result
Results for "
angiotensin I
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
1
Biochemical Assay Reagents
9
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-P1839A
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
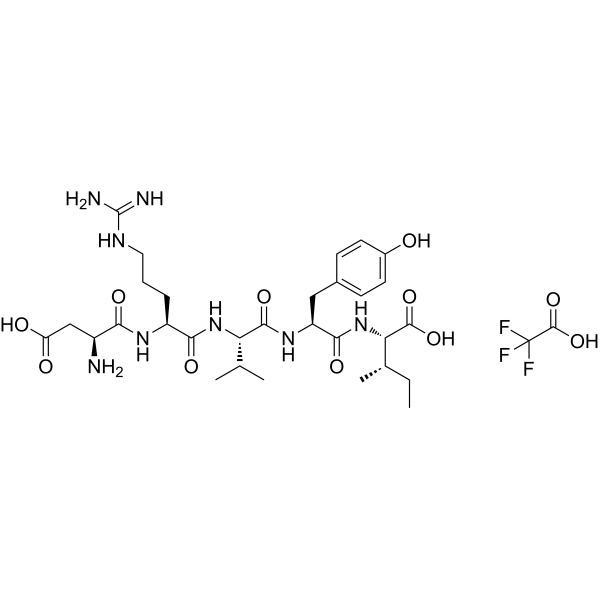
Angiotensin I/II 1-5 TFA is a peptide that contains the amino acids 1-5, which is converted from Angiotensin I/II. Angiotensin I is formed by the action of renin on angiotensinogen. Angiotensin II is produced from angiotensin I. Angiotensin II has been investigated for the treatment, basic science, and diagnostic of Hypertension, Renin Angiotensin System, and Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy .
|
-
-
- HY-P1829A
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
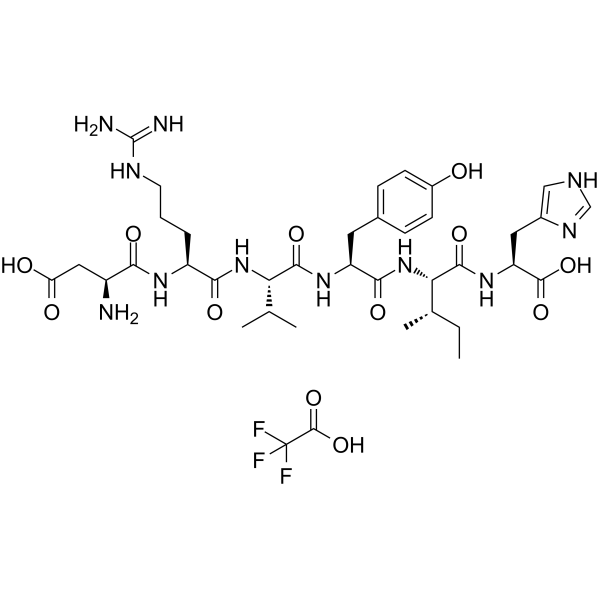
Angiotensin I/II (1-6) TFA contains the amino acids 1-6 and is converted from Angiotensin I/II peptide. The precursor angiotensinogen is cleaved by renin to form angiotensin I. Angiotensin I ishydrolyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to form the biologically active angiotensin II. Angiotensin II has been investigated for the treatment, basic science, and diagnostic of Hypertension, Renin Angiotensin System, and Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy .
|
-
-
- HY-P1032
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
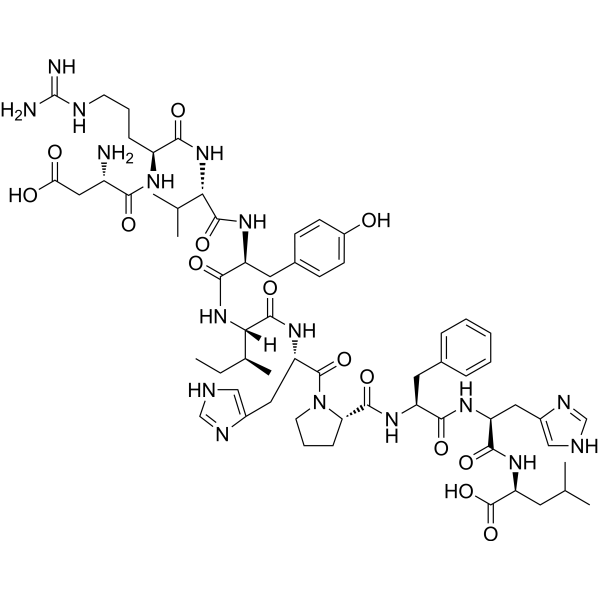
Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) is the precursor to the vasoconstrictor peptide angiotensin II, cleaved by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE).
|
-
-
- HY-P1839
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Angiotensin I/II 1-5 is a peptide that contains the amino acids 1-5, which is converted from Angiotensin I/II. Angiotensin I is formed by the action of renin on angiotensinogen. Angiotensin II is produced from angiotensin I. Angiotensin II has been investigated for the treatment, basic science, and diagnostic of Hypertension, Renin Angiotensin System, and Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy .
|
-
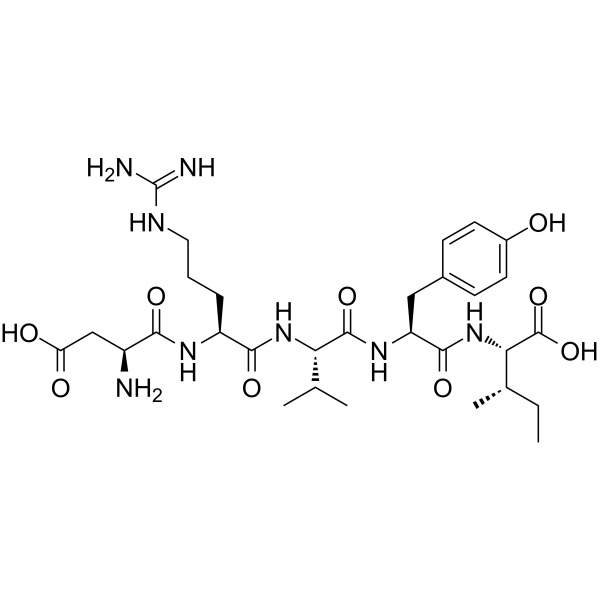
-
- HY-P1829
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Angiotensin I/II 1-6 contains the amino acids 1-6 and is converted from Angiotensin I/II peptide. The precursor angiotensinogen is cleaved by renin to form angiotensin I. Angiotensin I ishydrolyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to form the biologically active angiotensin II. Angiotensin II has been investigated for the treatment, basic science, and diagnostic of Hypertension, Renin Angiotensin System, and Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy .
|
-
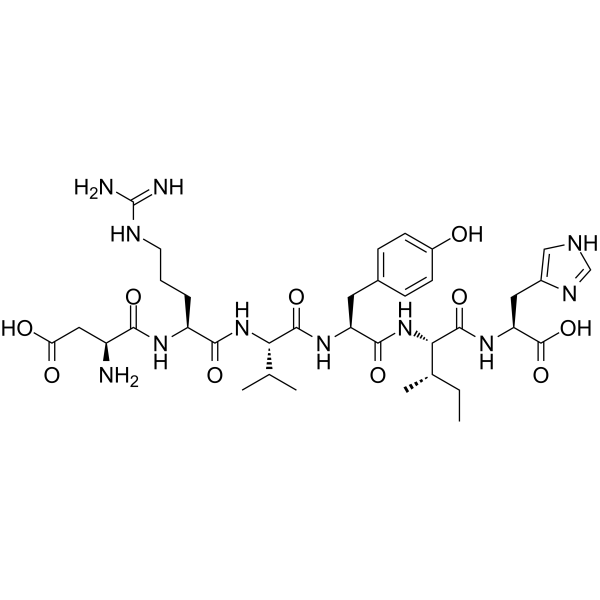
-
- HY-P2643
-
-
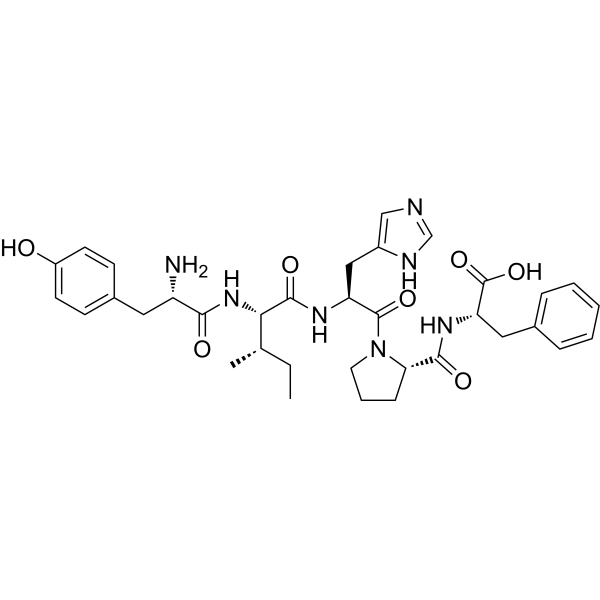
-
- HY-P1032S1
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Angiotensin I- 13C5, 15N (human, mouse, rat) is the 13C and 15N labeled Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) (HY-P1032). Citric acid is a natural preservative and food tartness enhancer. Citric acid induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and S phase in HaCaT cells. Citric acid cause oxidative damage of the liver by means of the decrease of antioxidative enzyme activities. Citric acid causes renal toxicity in mice .
|
-
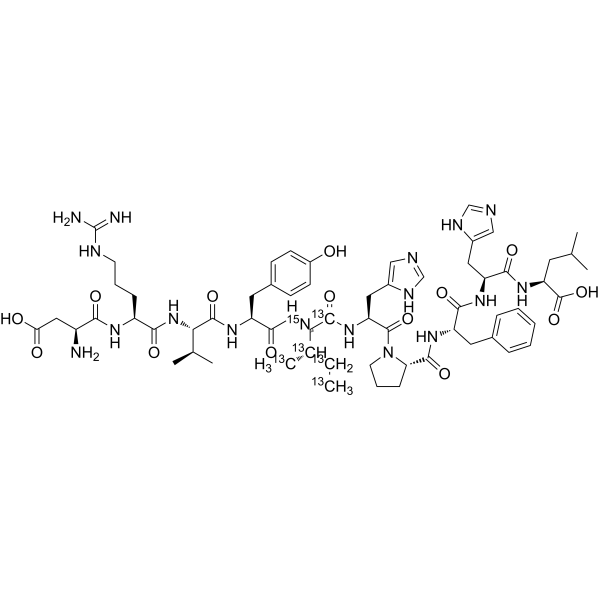
-
- HY-P1032S
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Angiotensin I- 13C19, 15N3 (human, mouse, rat) is the 13C and 15N labeled Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) (HY-P1032). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-
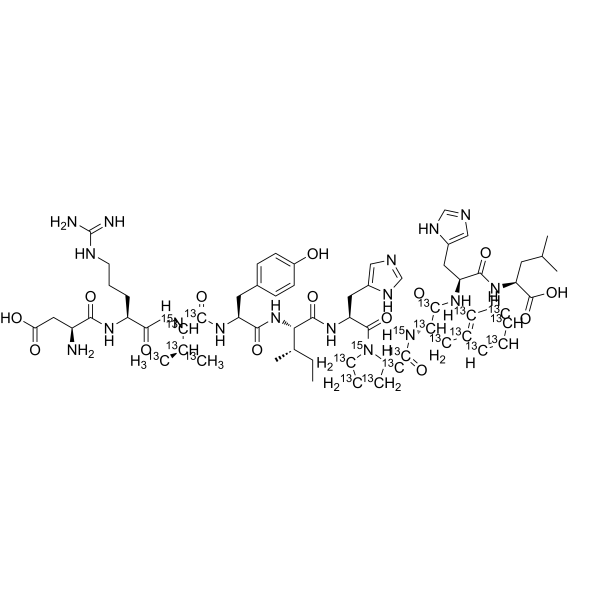
-
- HY-P1792
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Metabolic Disease
Endocrinology
|
|
Angiotensin II (1-4), human is an endogenous peptide produced from AT I by angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II binds the AT II type 1 (AT1) receptor, stimulating GPCRs in vascular smooth muscle cells and increasing intracellular Ca 2+ levels. Angiotensin II also acts at the Na +/H + exchanger in the proximal tubules of the kidney .
|
-
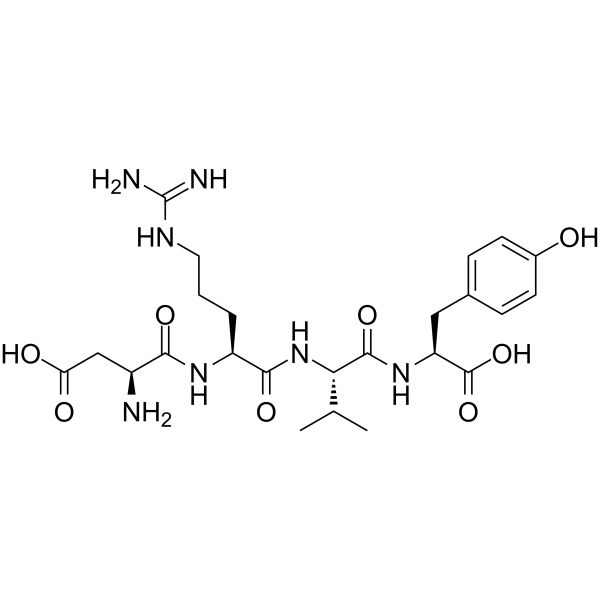
-
- HY-P1792A
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Metabolic Disease
Endocrinology
|
|
Angiotensin II (1-4), human (TFA) is an endogenous peptide produced from AT I by angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II binds the AT II type 1 (AT1) receptor, stimulating GPCRs in vascular smooth muscle cells and increasing intracellular Ca 2+ levels. Angiotensin II also acts at the Na +/H + exchanger in the proximal tubules of the kidney .
|
-
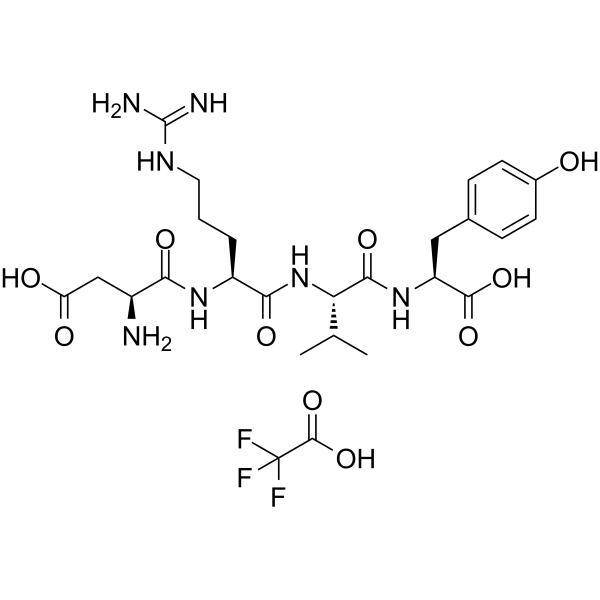
-
- HY-13948
-
|
angiotensin II; Ang II; DRVYIHPF
|
Angiotensin Receptor
Apoptosis
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Endocrinology
Cancer
|
|
Angiotensin II (Angiotensin II) is a vasoconstrictor and a major bioactive peptide of the renin/angiotensin system. Angiotensin II human plays a central role in regulating human blood pressure, which is mainly mediated by interactions between Angiotensin II and the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R). Angiotensin II human stimulates sympathetic nervous stimulation, increases aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions. Angiotensin II human induces growth of vascular smooth muscle cells, increases collagen type I and III synthesis in fibroblasts, leading to thickening of the vascular wall and myocardium, and fibrosis. Angiotensin II human also induces apoptosis. Angiotensin II induces capillary formation from endothelial cells via the LOX-1 dependent redox-sensitive pathway .
|
-
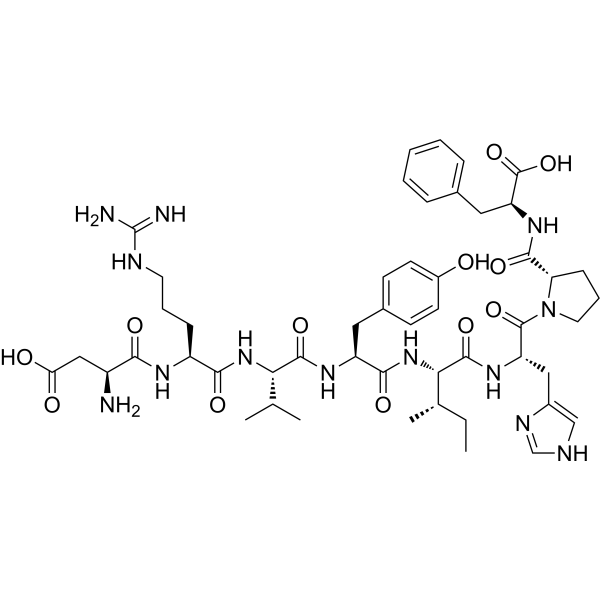
-
- HY-13948A
-
|
angiotensin II acetate; Ang II acetate; DRVYIHPF acetate
|
Angiotensin Receptor
Apoptosis
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Endocrinology
Cancer
|
|
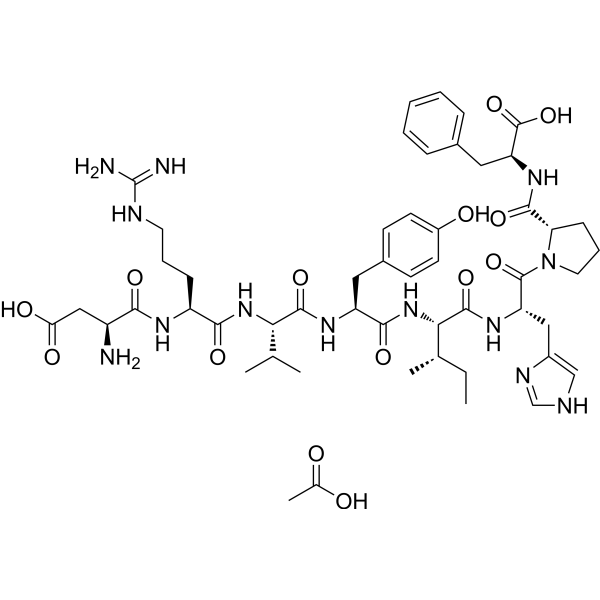
Angiotensin II human (Angiotensin II) acetate is a vasoconstrictor and a major bioactive peptide of the renin/angiotensin system. Angiotensin II human acetate plays a central role in regulating human blood pressure, which is mainly mediated by interactions between Angiotensin II and the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R). Angiotensin II human acetate stimulates sympathetic nervous stimulation, increases aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions. Angiotensin II human acetate induces growth of vascular smooth muscle cells, increases collagen type I and III synthesis in fibroblasts, leading to thickening of the vascular wall and myocardium, and fibrosis. Angiotensin II human acetate also induces apoptosis. Angiotensin II human acetate induces capillary formation from endothelial cells via the LOX-1 dependent redox-sensitive pathway .
|
-
-
- HY-13948B
-
|
angiotensin II TFA; Ang II TFA; DRVYIHPF TFA
|
Angiotensin Receptor
Apoptosis
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Endocrinology
Cancer
|
|
Angiotensin II human (Angiotensin II) TFA is a vasoconstrictor and a major bioactive peptide of the renin/angiotensin system. Angiotensin II human TFA plays a central role in regulating human blood pressure, which is mainly mediated by interactions between Angiotensin II and the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R). Angiotensin II human TFA stimulates sympathetic nervous stimulation, increases aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions. Angiotensin II human TFA induces growth of vascular smooth muscle cells, increases collagen type I and III synthesis in fibroblasts, leading to thickening of the vascular wall and myocardium, and fibrosis. Angiotensin II human TFA also induces apoptosis. Angiotensin II human TFA induces capillary formation from endothelial cells via the LOX-1 dependent redox-sensitive pathway .
|
-
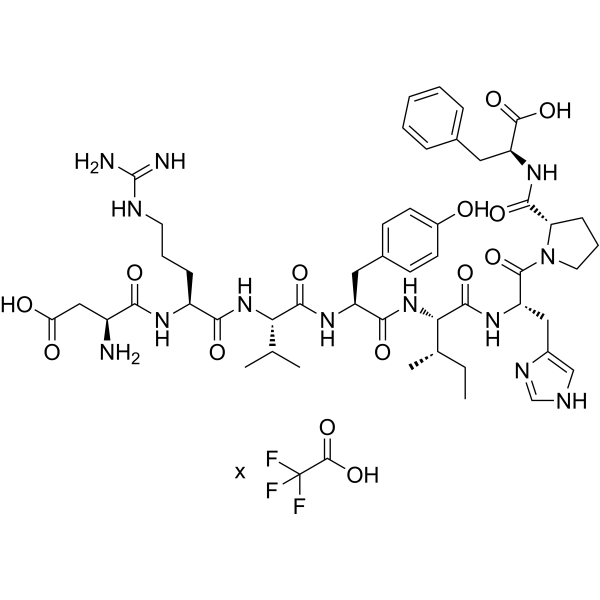
-
- HY-13948BS
-
|
angiotensin II-13C6,15N TFA; Ang II-13C6,15N TFA; DRVY(I-13C6,15N)HPF TFA
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Cancer
|
|
Angiotensin II human- 13C6, 15N TFA (Ang II- 13C6, 15N TFA) is 13C- and 15N-labeled Angiotensin II human (TFA) (HY-13948B). Angiotensin II human (Angiotensin II) TFA is a vasoconstrictor and a major bioactive peptide of the renin/angiotensin system. Angiotensin II human TFA plays a central role in regulating human blood pressure, which is mainly mediated by interactions between Angiotensin II and the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R). Angiotensin II human TFA stimulates sympathetic nervous stimulation, increases aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions .
|
-
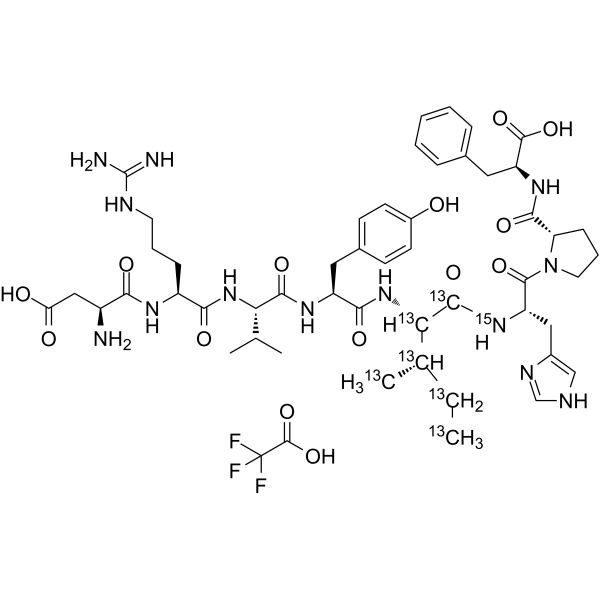
-
- HY-P1032F
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Endocrinology
|
|
Biotinyl-Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) is biotin-labeled Angiotensin I . Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) is the precursor to the vasoconstrictor peptide angiotensin II, cleaved by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) .
|
-
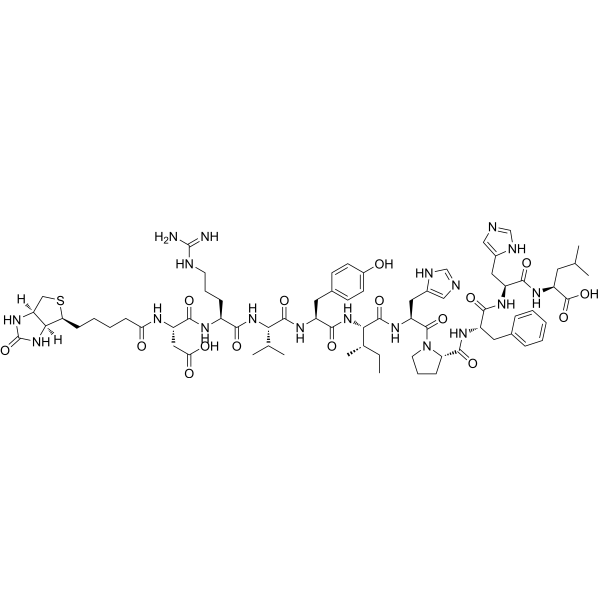
-
- HY-113681
-
-
-
- HY-139801
-
|
CI-907
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Metabolic Disease
|
|
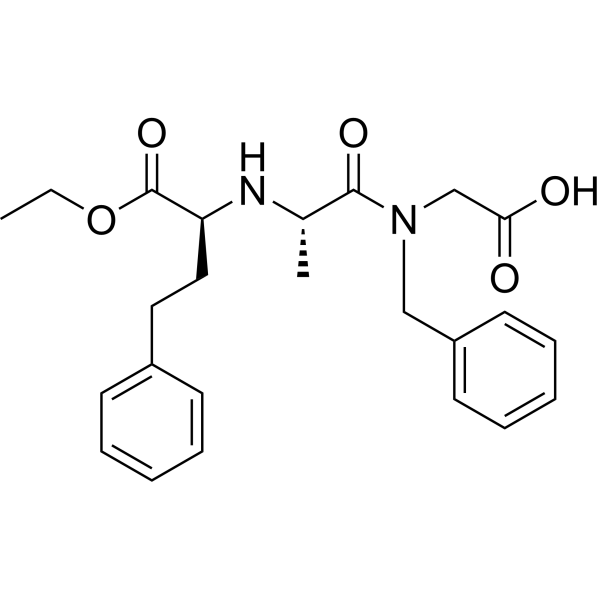
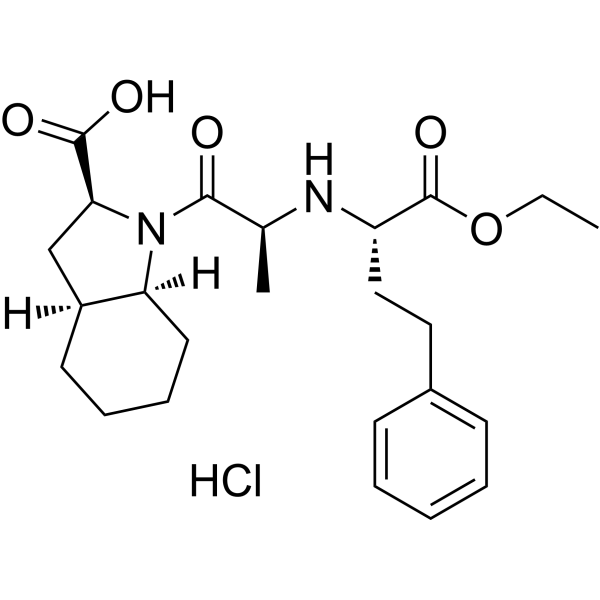
Indolapril hydrochloride (CI-907) is an orally active nonsulfhydryl angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Indolapril hydrochloride is highly specific in suppressing the contractile or pressor responses to Angiotensin I. Indolapril hydrochloride is a potent antihypertensive agent .
|
-
-
- HY-P2983
-
|
ACE; kininase II; CD143
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is a dicarboxypeptidase, it converts inactive Angiotensin I (Ang I) to active Ang II and degrades active bradykinin (BK). Angiotensin-converting enzyme is a potent vasoconstrictor, is often used in biochemical studies .
|
-
-
- HY-B0231
-
|
MK-422
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
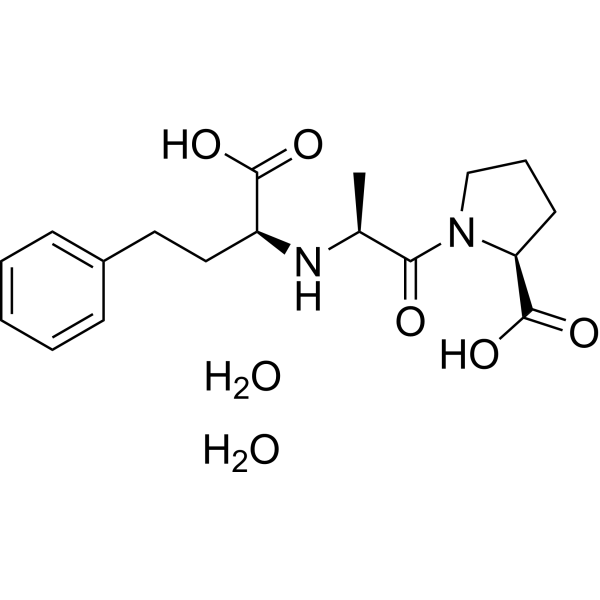
Enalaprilat dihydrate (MK-422), the active metabolite of the oral proagent Enalapril, is a potent, competitive and long-acting angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, with an IC50 of 1.94 nM. Enalaprilat dihydrate can be used for the research of hypertension .
|
-
-
- HY-B0231A
-
|
MK-422 anhydrous
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Enalaprilat (MK-422 anhydrous), the active metabolite of the oral proagent Enalapril, is a potent, competitive and long-acting angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, with an IC50 of 1.94 nM. Enalaprilat can be used for the research of hypertension .
|
-
-
- HY-127026A
-
|
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
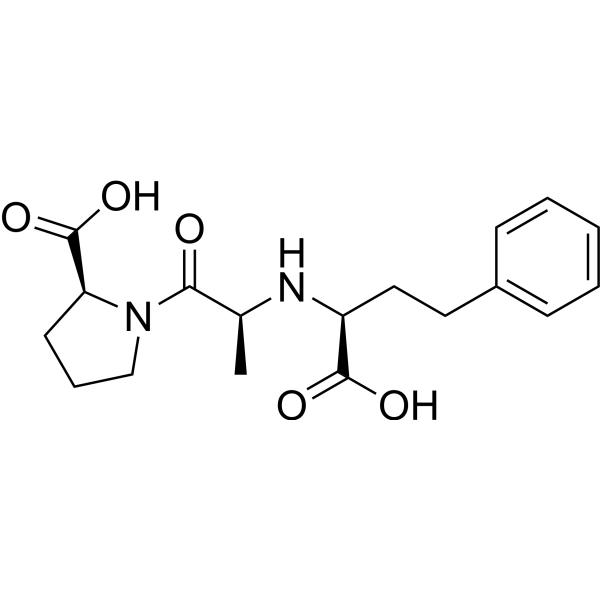
Quinaprilat hydrate is a non-mercapto Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, the active metabolite of Quinapril. Quinaprilat hydrate specifically blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II and inhibits the degradation of bradykinin. Quinaprilat hydrate acts as anti-hypertensive agent and vasodilator .
|
-
-
- HY-127026
-
|
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
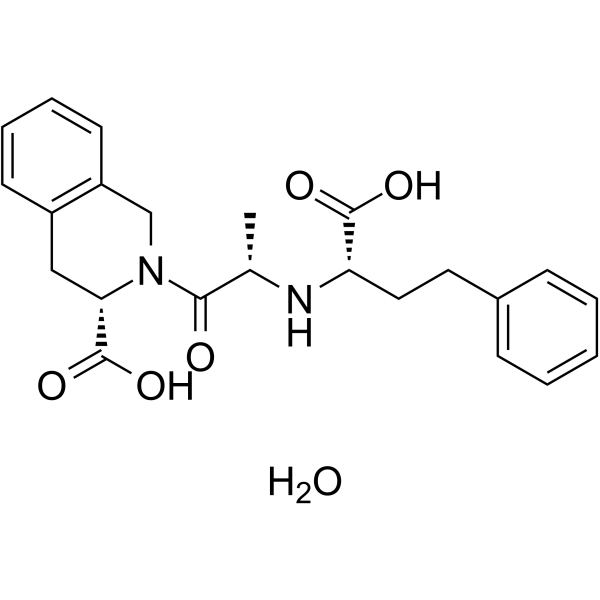
Quinaprilat is an orally active non-mercapto Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, the active metabolite of Quinapril. Quinaprilat specifically blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II and inhibits the degradation of bradykinin. Quinaprilat acts as anti-hypertensive agent and vasodilator .
|
-
-
- HY-A0230A
-
|
SCH 33844 hydrochloride
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
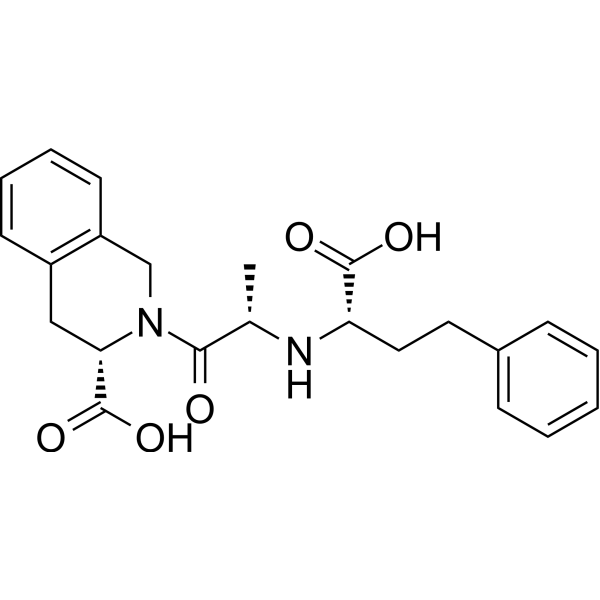
Spirapril (SCH 33844) hydrochloride is a potent angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with antihypertensive activity. Spirapril competitively binds to ACE and prevents the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Spirapril is an orally active proagent of Spiraprilat and can be used for the research of hypertension, congestive heart failure .
|
-
-
- HY-A0116A
-
|
Trandolaprilat hydrate; RU 44403 hydrate
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
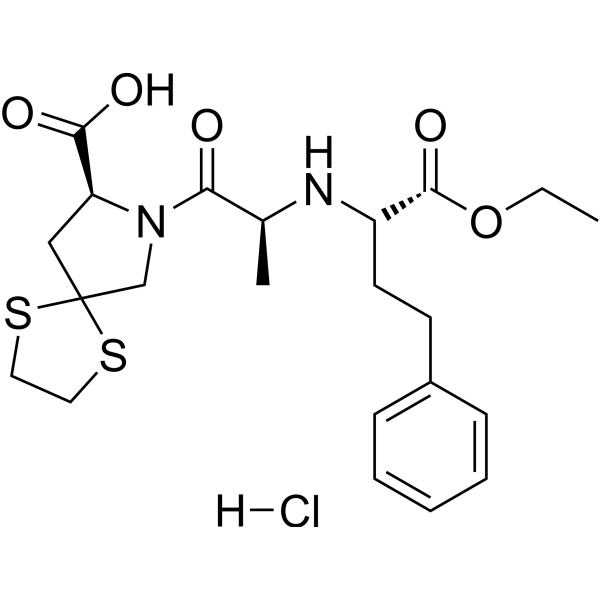
Trandolaprilate hydrate is a potent angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Trandolaprilate hydrate partially inhibits angiotensin-I-mediated c-fos induction. Trandolaprilate is main bioactive metabolite of Trandolapril. Trandolaprilate shows high lipophilicity .
|
-
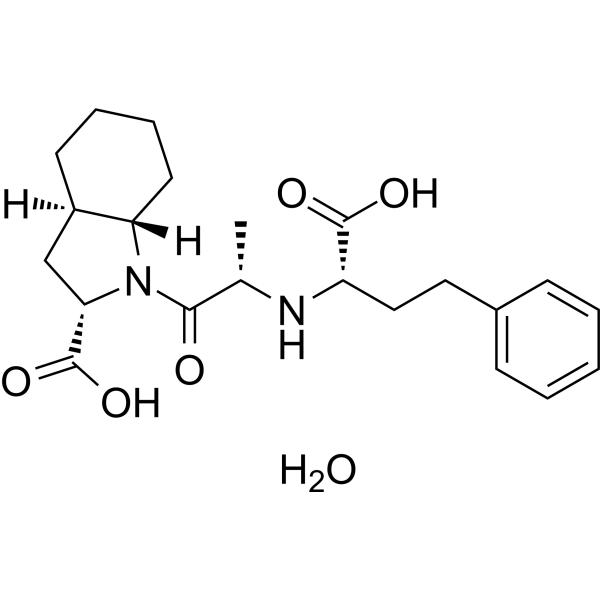
-
- HY-A0116
-
|
Trandolaprilat; RU 44403
|
|
|
|
Trandolaprilate is a potent angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Trandolaprilate partially inhibits angiotensin-I-mediated c-fos induction. Trandolaprilate is main bioactive metabolite of Trandolapril. Trandolaprilate shows high lipophilicity .
|
-
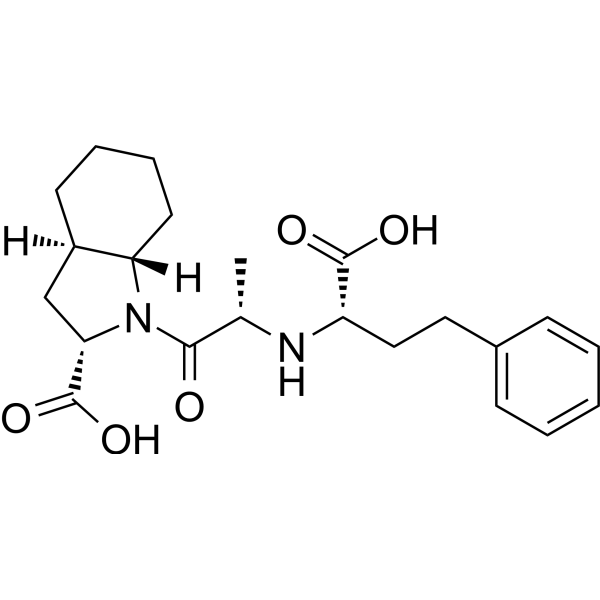
-
- HY-A0230
-
|
SCH 33844
|
|
|
|
Spirapril is a potent and cross the blood-brain barrier angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with antihypertensive activity. Spirapril competitively binds to ACE and prevents the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Spirapril is an orally active proagent of Spiraprilat and can be used for the research of hypertension, congestive heart failure .
|
-
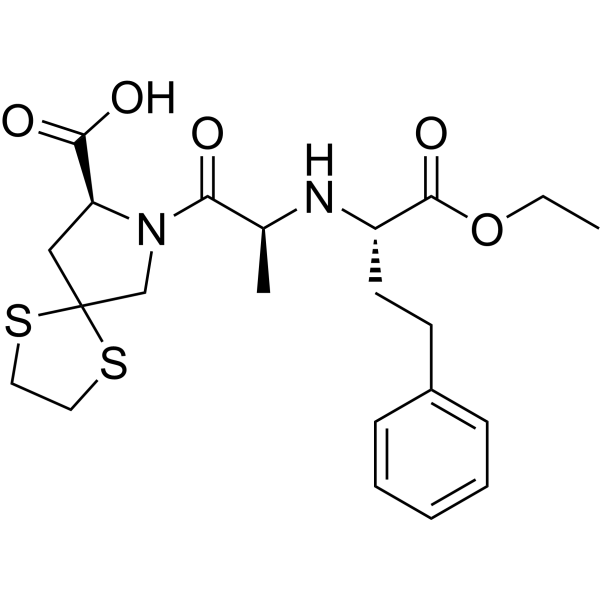
-
- HY-B1451
-
|
TA-6366
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
MMP
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Metabolic Disease
|
|
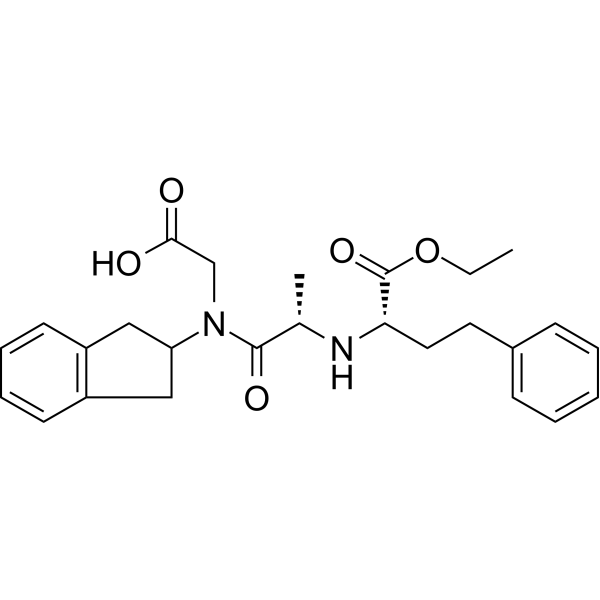
Imidapril hydrochloride (TA-6366) is an orally active angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and MMP-9 inhibitor. Imidapril hydrochloride suppresses the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II and thereby reduces total peripheral resistance and systemic blood pressure. Imidapril hydrochloride can be used for hypertension, type 1 diabetic, nephropathy and chronic heart failure research .
|
-
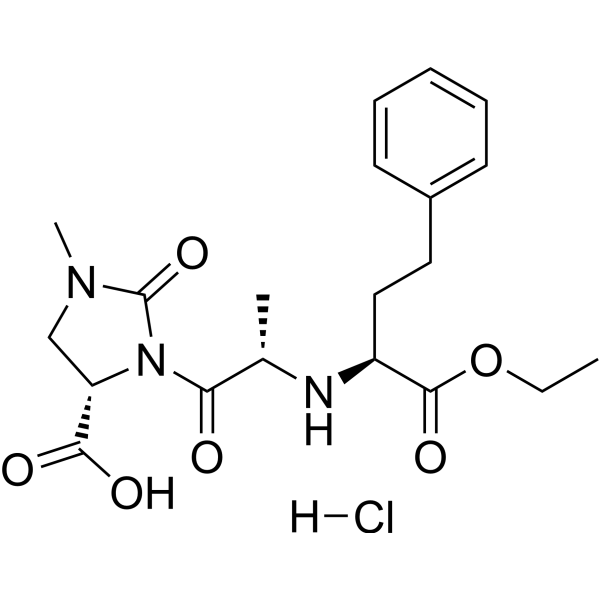
-
- HY-121232
-
-
-
- HY-B1451A
-
|
TA-6366 free base
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
MMP
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Metabolic Disease
|
|
Imidapril (TA-6366 free base) is an orally active angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and MMP-9 inhibitor. Imidapril suppresses the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II and thereby reduces total peripheral resistance and systemic blood pressure. Imidapril can be used for hypertension, type 1 diabetic, nephropathy and chronic heart failure research .
|
-
-
- HY-114161
-
-
-
- HY-114161A
-
-
-
- HY-A0116S1
-
|
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
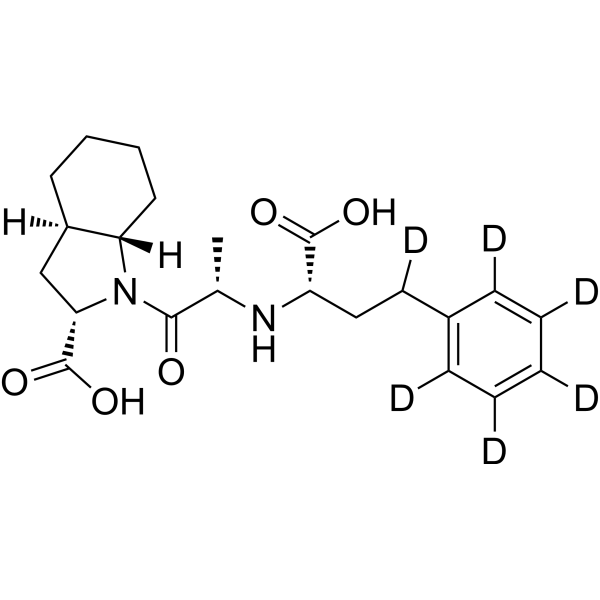
Trandolaprilate-d6 is the deuterium labeled Trandolaprilate[1]. Trandolaprilate is a potent angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Trandolaprilate partially inhibits angiotensin-I-mediated c-fos induction. Trandolaprilate is main bioactive metabolite of Trandolapril. Trandolaprilate shows high lipophilicity[2][3].
|
-
-
- HY-P1853
-
-
-
- HY-127026S
-
|
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
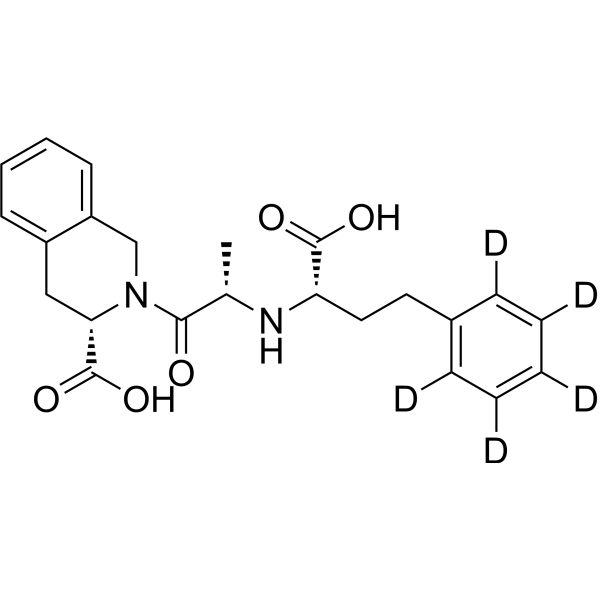
Quinaprilat-d5 is a deuterium-labeled Quinaprilat. Quinaprilat is a nonsulfhydryl ACE inhibitor, the active diacid metabolite of Quinapril. Quinaprilat specifically blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II and inhibits bradykinin degradation. Quinaprilat primarily acts as a vasodilator, decreasing total peripheral and renal vascular resistance[1].
|
-
-
- HY-13955
-
-
-
- HY-P10173
-
|
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Others
|
|
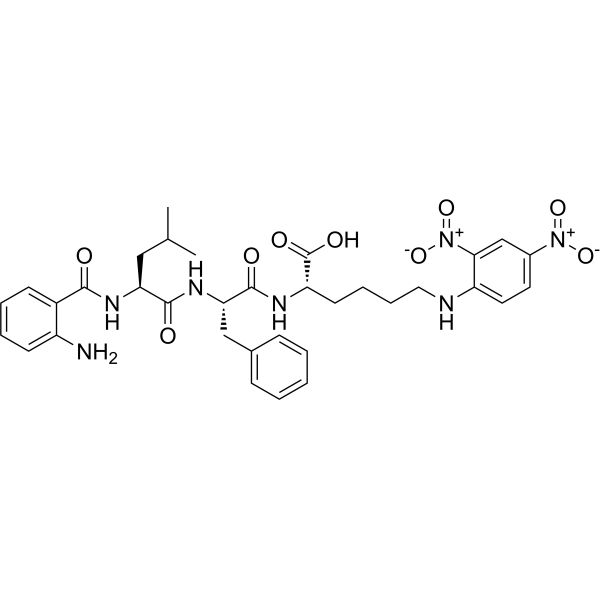
Abz-LFK(Dnp)-OH is an angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) peptide substrate. Abz-LFK(Dnp)-OH is selective for the C domain of ACE. Abz-LFK(Dnp)-OH can be used to assess ACE activity .
|
-
-
- HY-P3424
-
-
-
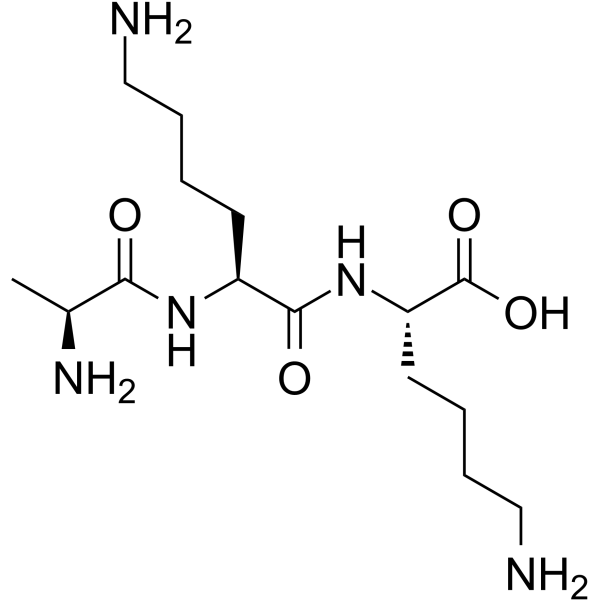
- HY-P4551
-
-
-
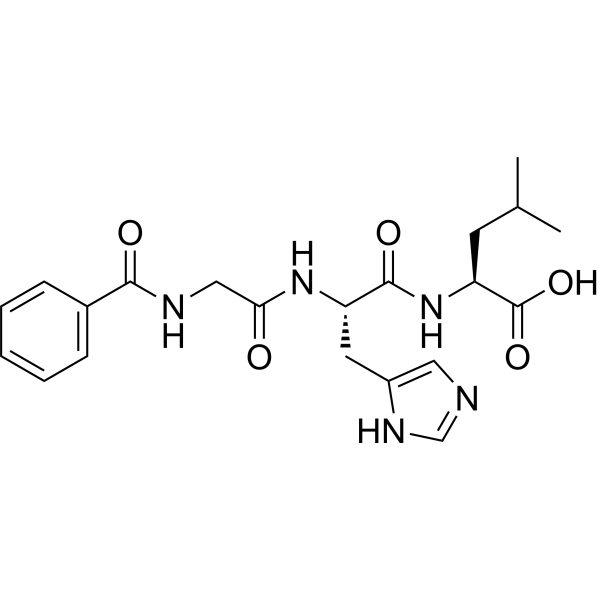
- HY-P10172
-
-
-
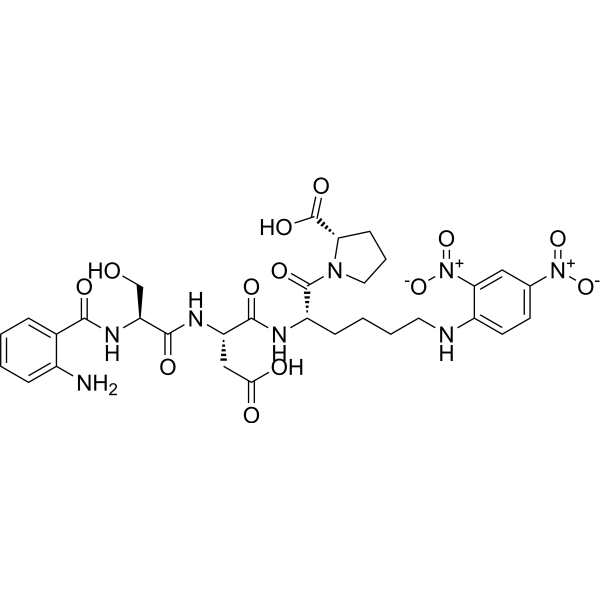
- HY-13955R
-
|
BIBR 277 (Standard)
|
Angiotensin Receptor
Autophagy
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Endocrinology
|
|
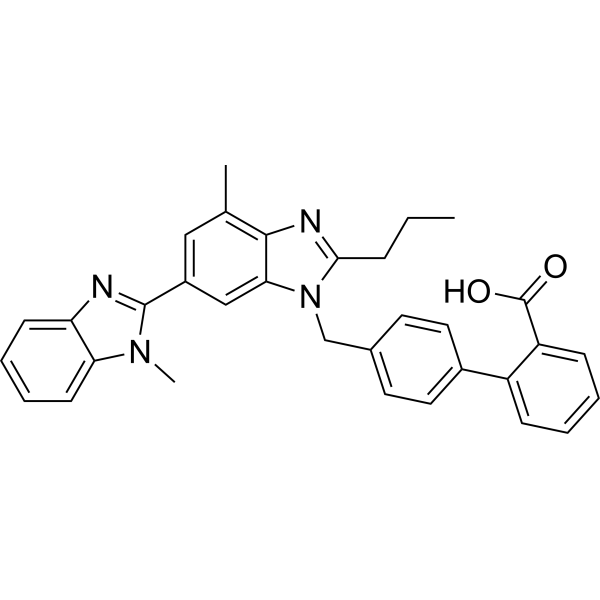
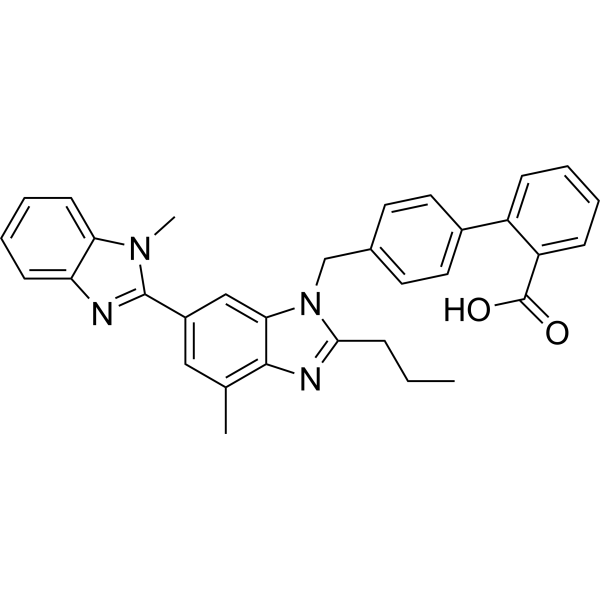
Telmisartan (Standard) is the analytical standard of Telmisartan. This product is intended for research and analytical applications. Telmisartan is a potent, long lasting antagonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1), selectively inhibiting the binding of 125I-AngII to AT1 receptors with IC50 of 9.2 nM.
|
-
-
- HY-13955S1
-
-
-
- HY-13955S
-
-
-
- HY-114782
-
|
L-Tyrosyl-L-tyrosine
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
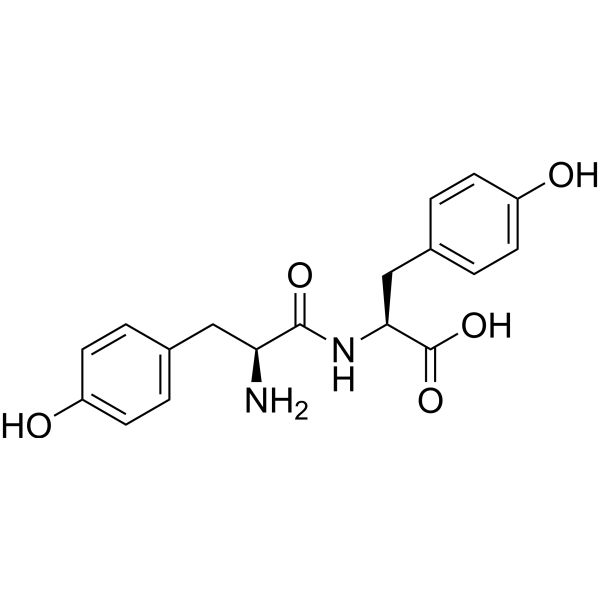
H-Tyr-Tyr-OH (L-Tyrosyl-L-tyrosine) is an antihypertensive peptide. H-Tyr-Tyr-OH inhibits angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) with an IC50 value of 0.028 mg/mL. H-Tyr-Tyr-OH can be used for the research of high blood pressure .
|
-
-
- HY-13955S2
-
-
-
- HY-13955S3
-
|
BIBR 277-d7
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
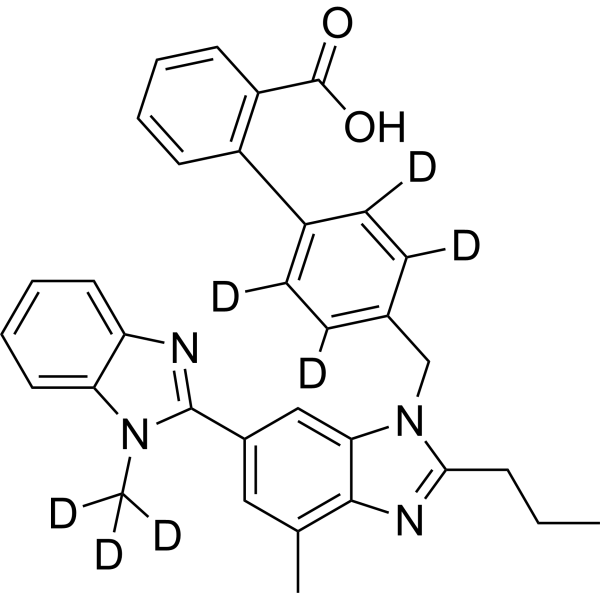
Telmisartan-d7 (BIBR 277-d7) is a deuterium labeled Telmisartan (HY-13955). Telmisartan is a potent, long lasting antagonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1), selectively inhibiting the binding of 125I-AngII to AT1 receptors with IC50 of 9.2 nM.
|
-
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-P2983
-
|
ACE; kininase II; CD143
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is a dicarboxypeptidase, it converts inactive Angiotensin I (Ang I) to active Ang II and degrades active bradykinin (BK). Angiotensin-converting enzyme is a potent vasoconstrictor, is often used in biochemical studies .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-P1839A
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Angiotensin I/II 1-5 TFA is a peptide that contains the amino acids 1-5, which is converted from Angiotensin I/II. Angiotensin I is formed by the action of renin on angiotensinogen. Angiotensin II is produced from angiotensin I. Angiotensin II has been investigated for the treatment, basic science, and diagnostic of Hypertension, Renin Angiotensin System, and Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy .
|
-
- HY-P1829A
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Angiotensin I/II (1-6) TFA contains the amino acids 1-6 and is converted from Angiotensin I/II peptide. The precursor angiotensinogen is cleaved by renin to form angiotensin I. Angiotensin I ishydrolyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to form the biologically active angiotensin II. Angiotensin II has been investigated for the treatment, basic science, and diagnostic of Hypertension, Renin Angiotensin System, and Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy .
|
-
- HY-P1032
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) is the precursor to the vasoconstrictor peptide angiotensin II, cleaved by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE).
|
-
- HY-P1839
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Angiotensin I/II 1-5 is a peptide that contains the amino acids 1-5, which is converted from Angiotensin I/II. Angiotensin I is formed by the action of renin on angiotensinogen. Angiotensin II is produced from angiotensin I. Angiotensin II has been investigated for the treatment, basic science, and diagnostic of Hypertension, Renin Angiotensin System, and Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy .
|
-
- HY-P1829
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Angiotensin I/II 1-6 contains the amino acids 1-6 and is converted from Angiotensin I/II peptide. The precursor angiotensinogen is cleaved by renin to form angiotensin I. Angiotensin I ishydrolyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to form the biologically active angiotensin II. Angiotensin II has been investigated for the treatment, basic science, and diagnostic of Hypertension, Renin Angiotensin System, and Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy .
|
-
- HY-P2643
-
-
- HY-P1032S1
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Angiotensin I- 13C5, 15N (human, mouse, rat) is the 13C and 15N labeled Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) (HY-P1032). Citric acid is a natural preservative and food tartness enhancer. Citric acid induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and S phase in HaCaT cells. Citric acid cause oxidative damage of the liver by means of the decrease of antioxidative enzyme activities. Citric acid causes renal toxicity in mice .
|
-
- HY-P1032S
-
|
|
Isotope-Labeled Compounds
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Others
|
|
Angiotensin I- 13C19, 15N3 (human, mouse, rat) is the 13C and 15N labeled Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) (HY-P1032). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-
- HY-P1792
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Metabolic Disease
Endocrinology
|
|
Angiotensin II (1-4), human is an endogenous peptide produced from AT I by angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II binds the AT II type 1 (AT1) receptor, stimulating GPCRs in vascular smooth muscle cells and increasing intracellular Ca 2+ levels. Angiotensin II also acts at the Na +/H + exchanger in the proximal tubules of the kidney .
|
-
- HY-P1792A
-
|
|
Angiotensin Receptor
|
Metabolic Disease
Endocrinology
|
|
Angiotensin II (1-4), human (TFA) is an endogenous peptide produced from AT I by angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II binds the AT II type 1 (AT1) receptor, stimulating GPCRs in vascular smooth muscle cells and increasing intracellular Ca 2+ levels. Angiotensin II also acts at the Na +/H + exchanger in the proximal tubules of the kidney .
|
-
- HY-13948
-
|
angiotensin II; Ang II; DRVYIHPF
|
Angiotensin Receptor
Apoptosis
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Endocrinology
Cancer
|
|
Angiotensin II (Angiotensin II) is a vasoconstrictor and a major bioactive peptide of the renin/angiotensin system. Angiotensin II human plays a central role in regulating human blood pressure, which is mainly mediated by interactions between Angiotensin II and the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R). Angiotensin II human stimulates sympathetic nervous stimulation, increases aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions. Angiotensin II human induces growth of vascular smooth muscle cells, increases collagen type I and III synthesis in fibroblasts, leading to thickening of the vascular wall and myocardium, and fibrosis. Angiotensin II human also induces apoptosis. Angiotensin II induces capillary formation from endothelial cells via the LOX-1 dependent redox-sensitive pathway .
|
-
- HY-13948A
-
|
angiotensin II acetate; Ang II acetate; DRVYIHPF acetate
|
Angiotensin Receptor
Apoptosis
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Endocrinology
Cancer
|
|
Angiotensin II human (Angiotensin II) acetate is a vasoconstrictor and a major bioactive peptide of the renin/angiotensin system. Angiotensin II human acetate plays a central role in regulating human blood pressure, which is mainly mediated by interactions between Angiotensin II and the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R). Angiotensin II human acetate stimulates sympathetic nervous stimulation, increases aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions. Angiotensin II human acetate induces growth of vascular smooth muscle cells, increases collagen type I and III synthesis in fibroblasts, leading to thickening of the vascular wall and myocardium, and fibrosis. Angiotensin II human acetate also induces apoptosis. Angiotensin II human acetate induces capillary formation from endothelial cells via the LOX-1 dependent redox-sensitive pathway .
|
-
- HY-13948B
-
|
angiotensin II TFA; Ang II TFA; DRVYIHPF TFA
|
Angiotensin Receptor
Apoptosis
|
Cardiovascular Disease
Endocrinology
Cancer
|
|
Angiotensin II human (Angiotensin II) TFA is a vasoconstrictor and a major bioactive peptide of the renin/angiotensin system. Angiotensin II human TFA plays a central role in regulating human blood pressure, which is mainly mediated by interactions between Angiotensin II and the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R). Angiotensin II human TFA stimulates sympathetic nervous stimulation, increases aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions. Angiotensin II human TFA induces growth of vascular smooth muscle cells, increases collagen type I and III synthesis in fibroblasts, leading to thickening of the vascular wall and myocardium, and fibrosis. Angiotensin II human TFA also induces apoptosis. Angiotensin II human TFA induces capillary formation from endothelial cells via the LOX-1 dependent redox-sensitive pathway .
|
-
- HY-P1032F
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Endocrinology
|
|
Biotinyl-Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) is biotin-labeled Angiotensin I . Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) is the precursor to the vasoconstrictor peptide angiotensin II, cleaved by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) .
|
-
- HY-P3545
-
|
|
Peptides
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
5-Valine-angiotensin I is an Ang I peptide belonging to angiotensin I. 5-Valine-angiotensin I induces muscle contraction, can be used for renin-angiotensin system studies. Angiotensin I is a putative neurotransmitter, is the precursor of angiotensin II and of angiotensin fragment 1-7, which are involved in regulation of fluid volume and the release of aldosterone .
|
-
- HY-P2983
-
|
ACE; kininase II; CD143
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is a dicarboxypeptidase, it converts inactive Angiotensin I (Ang I) to active Ang II and degrades active bradykinin (BK). Angiotensin-converting enzyme is a potent vasoconstrictor, is often used in biochemical studies .
|
-
- HY-P4545
-
|
|
Peptides
|
Others
|
|
Abz-Gly-p-nitro-Phe-Pro-OH is the fluorescent substrate angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE-I) with 355 nm excitation and 405 nm emission wavelengths .
|
-
- HY-P4552
-
|
|
Peptides
|
Others
|
|
Hippuryl-Phe-Arg-OH is the active site on the cell surface of Angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) .
|
-
- HY-114161
-
-
- HY-114161A
-
-
- HY-P1853
-
-
- HY-P10173
-
|
|
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
|
Others
|
|
Abz-LFK(Dnp)-OH is an angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) peptide substrate. Abz-LFK(Dnp)-OH is selective for the C domain of ACE. Abz-LFK(Dnp)-OH can be used to assess ACE activity .
|
-
- HY-P3424
-
-
- HY-P4551
-
-
- HY-P10172
-
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-13948
-
|
angiotensin II; Ang II; DRVYIHPF
|
Structural Classification
Natural Products
Classification of Application Fields
Source classification
Endogenous metabolite
Disease Research Fields
Endocrinology
Cancer
|
Angiotensin Receptor
Apoptosis
|
|
Angiotensin II (Angiotensin II) is a vasoconstrictor and a major bioactive peptide of the renin/angiotensin system. Angiotensin II human plays a central role in regulating human blood pressure, which is mainly mediated by interactions between Angiotensin II and the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R). Angiotensin II human stimulates sympathetic nervous stimulation, increases aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions. Angiotensin II human induces growth of vascular smooth muscle cells, increases collagen type I and III synthesis in fibroblasts, leading to thickening of the vascular wall and myocardium, and fibrosis. Angiotensin II human also induces apoptosis. Angiotensin II induces capillary formation from endothelial cells via the LOX-1 dependent redox-sensitive pathway .
|
-

-
- HY-A0116A
-
-

| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Chemical Structure |
-
- HY-13948BS
-
|
|
|
Angiotensin II human- 13C6, 15N TFA (Ang II- 13C6, 15N TFA) is 13C- and 15N-labeled Angiotensin II human (TFA) (HY-13948B). Angiotensin II human (Angiotensin II) TFA is a vasoconstrictor and a major bioactive peptide of the renin/angiotensin system. Angiotensin II human TFA plays a central role in regulating human blood pressure, which is mainly mediated by interactions between Angiotensin II and the G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R). Angiotensin II human TFA stimulates sympathetic nervous stimulation, increases aldosterone biosynthesis and renal actions .
|
-

-
- HY-P1032S1
-
|
|
|
Angiotensin I- 13C5, 15N (human, mouse, rat) is the 13C and 15N labeled Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) (HY-P1032). Citric acid is a natural preservative and food tartness enhancer. Citric acid induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and S phase in HaCaT cells. Citric acid cause oxidative damage of the liver by means of the decrease of antioxidative enzyme activities. Citric acid causes renal toxicity in mice .
|
-

-
- HY-P1032S
-
|
|
|
Angiotensin I- 13C19, 15N3 (human, mouse, rat) is the 13C and 15N labeled Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) (HY-P1032). Cellulose (Pectin glycosidase) is a natural high molecular weight polysaccharide found in many plants and organisms. It is widely used in manufacturing industries, such as in paper making, textiles, food and medicine, etc. As a renewable resource, Cellulose is biodegradable and sustainable, and can also be used to manufacture chemicals such as Cellulose Esters, Cellulose Acetate and Cellulose Nitrate. In addition, Cellulose is often used as a food additive to increase the stability and quality of food .
|
-

-
- HY-A0116S1
-
|
|
|
Trandolaprilate-d6 is the deuterium labeled Trandolaprilate[1]. Trandolaprilate is a potent angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Trandolaprilate partially inhibits angiotensin-I-mediated c-fos induction. Trandolaprilate is main bioactive metabolite of Trandolapril. Trandolaprilate shows high lipophilicity[2][3].
|
-

-
- HY-127026S
-
|
|
|
Quinaprilat-d5 is a deuterium-labeled Quinaprilat. Quinaprilat is a nonsulfhydryl ACE inhibitor, the active diacid metabolite of Quinapril. Quinaprilat specifically blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II and inhibits bradykinin degradation. Quinaprilat primarily acts as a vasodilator, decreasing total peripheral and renal vascular resistance[1].
|
-

-
- HY-13955S1
-
|
|
|
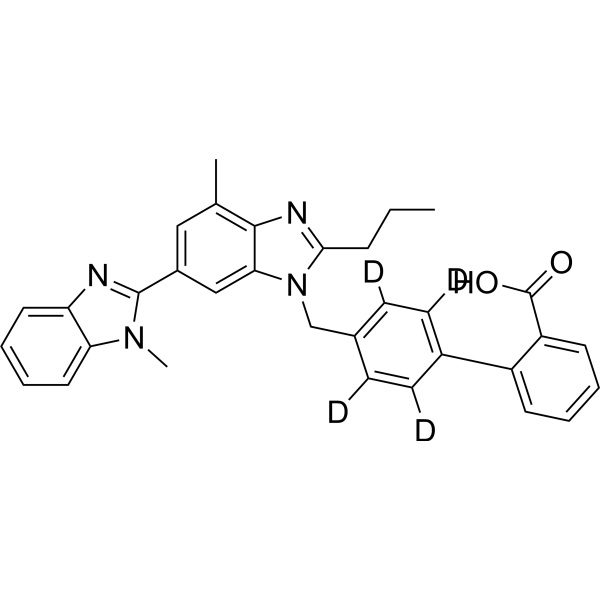
Telmisartan-d4 is the deuterium labeled Telmisartan. Telmisartan is a potent, long lasting antagonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1), selectively inhibiting the binding of 125I-AngII to AT1 receptors with IC50 of 9.2 nM[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-13955S
-
|
|
|
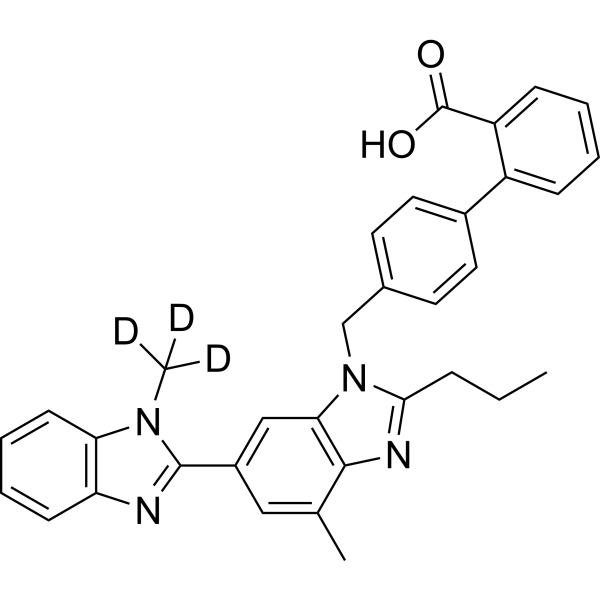
Telmisartan-d3 is the deuterium labeled Telmisartan. Telmisartan is a potent, long lasting antagonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1), selectively inhibiting the binding of 125I-AngII to AT1 receptors with IC50 of 9.2 nM[1][2].
|
-

-
- HY-13955S2
-
|
|
|
Telmisartan- 13C,d3 is the 13C- and deuterium labeled Telmisartan. Telmisartan is a potent, long lasting antagonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1), selectively inhibiting the binding of 125I-AngII to AT1 receptors with IC50 of 9.2 nM.
|
-

-
- HY-13955S3
-
|
|
|
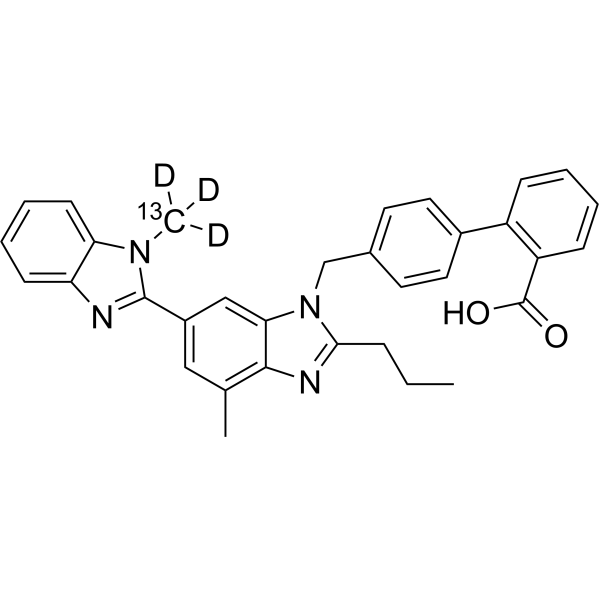
Telmisartan-d7 (BIBR 277-d7) is a deuterium labeled Telmisartan (HY-13955). Telmisartan is a potent, long lasting antagonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1), selectively inhibiting the binding of 125I-AngII to AT1 receptors with IC50 of 9.2 nM.
|
-

| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Application |
Reactivity |
-
- HY-P80003
-
|
ACE-2; ACE 2; angiotensin converting enzyme 2; ACE related carboxypeptidase; ACEH; angiotensin converting enzyme homolog; angiotensin converting enzyme like protein; angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (peptidyl dipeptidase A) 2; angiotensin I converting enzyme 2; DKFZP434A014; EC 3.4.17; angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 precursor; ACE2_HUMAN; angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ACE-related carboxypeptidase; angiotensin-converting enzyme homolog; Metalloprotease MPROT15; Processed angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
|
WB, ICC, IHC-P, IP
|
Human, Mouse, Hamster |
|
ACE2 Antibody is a non-conjugated and Rabbit origined monoclonal antibody about 92 kDa, targeting to ACE2. It can be used for WB,ICC,IHC-P,IP assays with tag free, in the background of Human, Mouse, Hamster.
|
-
- HY-P81084
-
|
angiotensin Converting Enzyme 1; ACE; ACE-T; angiotensin-converting enzyme isoform 1precursor; Dipeptidyl carboxy peptidase 1; Kininase II; ACE-1; testis-specific isoform precursor. ACE 1; ACE T; ACE1; angiotensin converting enzyme somatic isoform; angiotensin converting enzyme testis specific isoform; angiotensin I converting enzyme; angiotensin I converting enzyme 1; angiotensin I converting enzyme peptidyl dipeptidase A 1; Carboxycathepsin; CD 143; CD143; CD143 antigen; DCP 1; DCP; DCP1; Dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase 1; MVCD3; Peptidase P; Peptidyl dipeptidase A; Testicular ECA; ACE_HUMAN.
|
WB; ELISA; IHC-P; IHC-F; ICC; IF
|
Human, Mouse, Rat(predicted: Dog, Pig, Cow, Sheep) |
|
ACE Antibody is an unconjugated, approximately 147 kDa, rabbit-derived, anti-ACE polyclonal antibody. ACE Antibody can be used for: WB, ELISA, IHC-P, IHC-F, ICC, IF expriments in human, mouse, rat, and predicted: dog, pig, cow, sheep background without labeling.
|
-
- HY-P82349
-
|
ACE; Dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase I; Kininase II
|
WB, IHC-P
|
Mouse, Rat |
Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: